Registration Policy
Registration Policy
注册账号
部分本平台服务仅向注册用户提供,如果您使用本平台提供的网络存储空间进行视听、文字等内容的上传及传播等,请先根据本协议及其他本平台规则提示的规则、流程注册成为注册用户,并确保注册信息的真实性、正确性及完整性,如果上述注册信息发生变化,您应及时更改。
您应对注册获得的本平台账号(以下简称“账号”)项下的一切行为承担全部责任,不得侵犯包括但不限于本平台在内的任何主体的合法权益。
您理解并同意,您仅享有账号及账号项下由本平台提供的虚拟产品及服务的使用权,账号及该等虚拟产品及服务的所有权归本平台所有(法律法规另有规定的除外)。未经本平台书面同意,您不得以任何形式处置账号的使用权(包括但不限于赠与、出借、转让、销售、抵押、继承、许可他人使用)。如果本平台发现或者有合理理由认为使用者并非账号初始注册人,本平台有权在不通知您的情况下,暂停或终止向该注册账号提供服务,并注销该账号。
您应妥善保管账号信息、账号密码以及其他与账号相关的信息、资料。如因您的原因,造成账号信息、资料、数据的变动、灭失或财产损失等,您应立即通知本平台并自行承担相关法律后果。
本平台上的内容
本平台上的内容是指经由本平台提供的服务,以上传、张贴或任何其他方式传送或传播的任何资讯、资料、文字、软件、音乐、音频、照片、图形、视频、信息、链接或其他资料,无论系公开还是私下传送(以下简称“内容”),内容提供者、上传者应对其提供、上传的内容承担全部责任,如果给本平台造成损失的,还应向本平台承担赔偿责任。对于第三方因用户上传的内容向本平台主张权利的,本平台有权在不事先通知内容提供者、上传者的情况下直接采取删除、屏蔽、断开链接等必要措施。
您应对注册获得的本平台账号(以下简称“账号”)项下的一切行为承担全部责任,不得侵犯包括但不限于本平台在内的任何主体的合法权益。
您理解并同意,您仅享有账号及账号项下由本平台提供的虚拟产品及服务的使用权,账号及该等虚拟产品及服务的所有权归本平台所有(法律法规另有规定的除外)。未经本平台书面同意,您不得以任何形式处置账号的使用权(包括但不限于赠与、出借、转让、销售、抵押、继承、许可他人使用)。如果本平台发现或者有合理理由认为使用者并非账号初始注册人,本平台有权在不通知您的情况下,暂停或终止向该注册账号提供服务,并注销该账号。
您应妥善保管账号信息、账号密码以及其他与账号相关的信息、资料。如因您的原因,造成账号信息、资料、数据的变动、灭失或财产损失等,您应立即通知本平台并自行承担相关法律后果。
本平台上的内容
本平台上的内容是指经由本平台提供的服务,以上传、张贴或任何其他方式传送或传播的任何资讯、资料、文字、软件、音乐、音频、照片、图形、视频、信息、链接或其他资料,无论系公开还是私下传送(以下简称“内容”),内容提供者、上传者应对其提供、上传的内容承担全部责任,如果给本平台造成损失的,还应向本平台承担赔偿责任。对于第三方因用户上传的内容向本平台主张权利的,本平台有权在不事先通知内容提供者、上传者的情况下直接采取删除、屏蔽、断开链接等必要措施。
您在本平台上传或发布的内容,您保证对其享有合法的著作权或相应授权,本平台有权展示、散布及推广前述内容。
为提高您内容曝光量及发布效率,本平台将额外为您提供全球范围内的展示和推广服务,您同意您在本平台的账号所发布的全部内容均授权本平台以您的账号同步至本平台运营的全部产品,包括但不限于PC、平板、手机、电视、机顶盒、可穿戴设备等全部客户端软件和/或网站。同时,您允许本平台在同步并展示内容时可自行或委托第三方进行必要的处理(包括但不限于翻译、汇编、改编等)。您在此确认并同意,本平台有权自行或委托第三方在与上述内容、本平台产品及相关服务、本平台和/或本平台品牌有关的任何宣传、推广和/或研究中以适当的方式开发和使用上述内容(全部或部分)。
Silica magnetic beads can bind nucleic acids controlled by three competing effects: weak electrostatic repulsion forces, dehydration, hydrogen bond formation(Melzak et al., 1996). By the support of guanidine salts, detergents, or proteinase K, the nucleic acids are released from the biological samples, such as cell, tissues, plant and microorganism. Consequently, the released nucleic acids specially bind to silica magnetic beads forming DNA/RNA-beads complexes under the condition of chaotropic salts (e.g. guanidine salts, perchlorate salts and isopropanol etc.). Through magnetic separation, the complexes can be rapidly collected from the biological sample lysis solution. Proteins, other impurities and any salts are washed away by several washing steps with different washing buffers. Finally, the pure DNA/RNA can be easily eluted from the beads by TE(10mM Tris, 1mM EDTA, pH8.0) or ddH2O(pH>7.0). From the basic principle described above, we can get the optimal reagents and operating process by adjusting parameters including pH value, salt concentration, kind of chaotropic or kosmotropic salt, detergent concentration, which involve the lysis buffer, binding buffer, washing buffer and elution buffer.
At present, the chemical constituents in nucleic acids isolation kits differ from different company, but all these kits are mainly divided into two groups, chaotropic salt system(Boom et al., 1990), kosmotropic salts system(Lee et al., 2008), according to the salts used for binding. The chaotropic salts, such as iodized salts, perchlorate, and guanidine salts, which have the ability to disrupt the regular hydrogen bond structures. The high concentration of chaotropic salts let proteins denature, nucleicacidase lose activity, and help silica magnetic beads selectively bind nucleic acids. In contrast, the Kosmotropic salts have much stronger interactions with water and promote hydrophobic interactions, these including sodium sulfate and ammonium sulfate, etc.
The novel method of nucleic acids isolation based on silica beads can be used to extract DNA/RNA with different length from wide varieties of biological samples. For examples, isolation genomic DNA from plant(Zhang et al., 2007), fungi(Rittich et al., 2006), blood(Duarte et al., 2010), forensic tissue(Nagy et al., 2005); and isolation RNA from cells(Lee et al., 2008), plant(Ding et al., 2008); and isolation plasmid DNA from bacterial cells(Chiang et al., 2006); meanwhile certain reagents match silica magnetic beads for DNA/RNA isolation also listed in these referred publications.
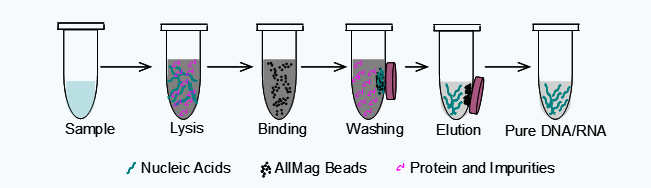
Fig. The sketch of application of silica magnetic beads on nucleic acids isolation
References
Boom R., Sol C., Salimans M., Jansen C., Wertheim-van Dillen P., Van der Noordaa J. (1990) Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 28:495.
Chiang C.L., Sung C.S., Chen C.Y. (2006) Application of silica-magnetite nanocomposites to the isolation of ultrapure plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 305:483-490.
Ding L.-W., Sun Q.-Y., Wang Z.-Y., Sun Y.-B., Xu Z.-F. (2008) Using silica particles to isolate total RNA from plant tissues recalcitrant to extraction in guanidine thiocyanate. Analytical Biochemistry 374:426-428.
Duarte G.R.M., Price C.W., Littlewood J.L., Haverstick D.M., Ferrance J.P., Carrilho E., Landers J.P. (2010) Characterization of dynamic solid phase DNA extraction from blood with magnetically controlled silica beads. Analyst 135:531-537.
Lee M., Huh N., Kim J.H. (2008) Isolation of total RNA from Escherichia coli using kosmotropic Hofmeister salts. Analytical Biochemistry 381:160-162. DOI: Doi 10.1016/J.Ab.2008.06.015.
Ligozzi M., Fontana R. (2003) Isolation of total DNA from bacteria and yeast. African Journal of Biotechnology 2:251-253.
Melzak K., Sherwood C., Turner R., Haynes C. (1996) Driving forces for DNA adsorption to silica in perchlorate solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 181:635-644.
Nagy M., Otremba P., Krüger C., Bergner-Greiner S., Anders P., Henske B., Prinz M., Roewer L. (2005) Optimization and validation of a fully automated silica-coated magnetic beads purification technology in forensics. Forensic Science International 152:13-22.
Rittich B., Spanova A., Horak D., Benes M.J., Klesnilova L., Petrova K., Rybnikar A. (2006) Isolation of microbial DNA by newly designed magnetic particles. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces 52:143-148. DOI: DOI 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.04.012.
Zhang Z.C., Cui Y., Wan Q.H. (2007) Surface modification of magnetic silica microspheres and its application to the isolation of plant genomic nucleic acids. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry 35:31-36.